The legal framework in the Republic of North Macedonia that regulates the cultural processes and work of its institutions consists of a set of laws, by-laws, strategies and yearly strategic operating plans of the Ministry of Culture.
The main law in the field of culture is the Law on Culture (1998) which was meant to be a unified law on the cultural field. When it was passed in 1998, partial co-ordination was achieved between the existing constitutional system and the new social, political and economic conditions in the country. It also guaranteed the freedom of creative work and related rights; made possible the introduction of a civil concept of culture; an equal status for public and private entities that work in the field of culture; introduction of a decentralised system for culture; financing activities in the “national interest” through an open competition, etc. However, it is important to note that past experience with the Law on Culture revealed many weaknesses and pointed out the necessity for amendments. It became clear that a re-evaluation of the Law on Culture was necessary. Subsequently, the Law on Culture was amended 17 times.
The National Strategy for Cultural Development stated that the Law on Culture has become old-fashioned, rigid and anachronous. According to this Strategy a new Law on exercising the public interest in culture was prepared (2019) and awaits the Parliamentary procedure.
Table 9: Legislation on culture
| Title of the act | Year of adoption |
| Law on Compulsory Deposits to the National Library | 1994 (amended 2008/2011) |
| Law on Copyright and Related Rights | 2010 (amended 2011/2015) |
| Law on the Use of the Macedonian Language | 1998 (amended 1998/2003/ 2005/2008/2010/2013/ 2015/2017) |
| Law on Culture | 1998 (amended 1998/2003/2005/ 2007/2010/2011/2012/2013/ 2014/2015/2016/2018) |
| Law on Protection of Cultural Heritage | 2004 (amended 2004/2007/2011/2013/2014/ 2015/2016/2018) |
| Law on Museums | 2004 (amended 208, 2010, 2011/2015/2016 |
| Law on Libraries | 2004 (amended 2008/2010/2011/2015/2016) |
| Law on Memorial Monuments and Commemorative Sites | 2004 (amended 2008/2015) |
| Media Law | 2005 |
| Law on the Film Fund | 2006 (amended 2008, 2011, 2012) |
| Law on Publishing | 2014 (amended 2015) |
| Law on Audio-visual Goods | 2008 amended 2011 |
| Law on the Protection of the Skopje Old Bazaar as a significant cultural monument | 2008 amended 2010 |
| Law on Copyright and Related Rights | 2010 |
| Law on Governing of the World Natural and Cultural Heritage in the Ohrid Region | 2011 (amended 2015) |
| Law on the National Artists of the Republic of Macedonia | 2011 (annuled 2017) |
| Law on the Protection of the old town centre of Krusevo as significant cultural heritage | 2012 |
| Law on the Support of Domestic Music Production | 2013 (annuled 2018) |
| Law on Film | 2013 (amended 2014/2015/2016/2018) |
| Law on State Awards | 2006 (amended 2007) |
| Law on Audiovisual Goods | 2008 (amended 2011/2016) |
| Law on the Protection of the old town centre of Kratovo as significant cultural heritage | 2014 |
| Law on the Protection of the old town centre of Bitola as significant cultural heritage | 2015 |
The Republic of North Macedonia has ratified the following UN conventions which are under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Culture:
- Convention for the Protection of Cultural Property in the Event of Armed Conflict with Regulations for the Execution of the Convention.
- Convention on the Means of Prohibiting and Preventing the Illicit Import, Export and Transfer of Ownership of Cultural Properties.
- Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage.
- Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage.
- Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions.
- Universal Copyright Convention, with Appendix Declaration relating to Articles XVII and Resolution concerning Article XI and Universal Copyright Convention as revised in Paris on July 24, 1971, with an Appendix Declaration relating to Article XVII and the Resolution concerning Article XI.
- Convention for the Protection of Producers of Phonograms against Unauthorized Duplication of their Phonograms.
- Convention Establishing the World Intellectual Property Organization.(Source: Ministry of Culture)
The Republic of North Macedonia has been a member of UNESCO since 28 June 1993. It ratified various conventions including the Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions (2007) and the Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage (2006). Between 2016 and 2017, UNESCO’s Participation Programme approved 5 projects that MK participated in, including 1 regional project. Lake Ohrid region is a World Heritage Site since 1979. Bitola became a UNESCO Creative City of Film in 2015 (part of UNESCO Creative Cities Network). The country is included in the UNESCO/EU action to Fight Illicit Trafficking of Cultural Property.
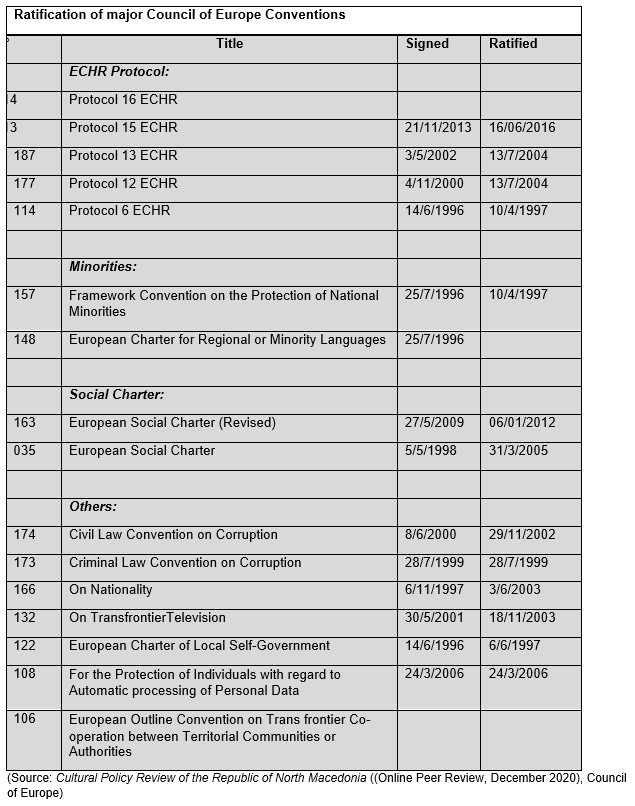
Table 10: Relations with the Council of Europe
| Date of application | 13 May 1993: Special Guest Status with the Assembly 25 June 1993: Date of candidature for accession |
| Accession | 9 November 1995 Opinion 191 (1995) Application by “the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia”* for membership of the Council of Europe |
| Ratification ECHR | 10 April 1997 |
| Relations with the Court | Judge to the European Court of Human Rights: Jovan Ilievski (since February 2017). The Court dealt with 257 applications concerning “The Republic of North Macedonia” in 2019, of which 246 were declared inadmissible or struck out. It delivered 12 judgments (concerning 11 applications), 9 of which found at least one violation of the ECHR. ECtHR/Country Profile (last updated: July 2020) |
| Execution of Judgements of the ECHR | Country Factsheet – North Macedonia (updated: October 2020) |
| Signature/Ratification CoE Conventions | To date, North Macedonia has signed and ratified the following (95) conventions. To date, North Macedonia has signed but not ratified the following (9) conventions. To date, North Macedonia has neither signed nor ratified the following (104) conventions. |
(Source: Cultural Policy Review of the Republic of North Macedonia ((Online Peer Review, December 2020), Council of Europe)

Comments are closed.